Anomaly Detection Simplified
In statistics and data mining, anomalies are data points, events or observations that do not conform to the expected pattern of the given data set. Detecting anomalies would mean that we need to raise flag for these deviations and validate these against business rules and constraints.
Anomalies creep into data sets by faulty systems capturing the data, or events that aren’t likely to happen on a regular day. For example, a fraudulent transaction in banking system could creep into dataset as an anomaly and it’d become paramount to detect these to avoid loss of revenue. A machine malfunctioning would send in anomalous data to the system via it’s sensor and a timely detection of these could help us reduce machine downtime and loss in production output. Another example where anomalies become a crease that needs to smoothen out would be, detect malicious software. These malicious software, if left undetected could crash multi-billion-dollar systems and bring the economy to a standstill.
Before we get into understanding of machine learning techniques to filter out anomalous data points, it’ll be helpful if we wrap our heads around a broad classification of machine learning techniques. We can classify these intelligence methods into two broad categories: supervised and unsupervised learning. Supervised learning is used when we have historical datasets, manually and methodically labeled to classify observations into normal events and abnormal events (1’s and 0’s). Unsupervised learning is applied when we don’t know what we are looking for in the data. For the scope of this blog we’ll be discussing unsupervised anomaly detection only.
Unsupervised Anomaly Detection:
It is often the case—especially when a company isn’t well established, or they’ve started a new business—there’s a paucity of labeled data. When this happens machine learning algorithms of decision trees and logistic regression fail. Data scientist must build models that can work without human supervision and detect anomalous observations, raising red flags when such an event occurs.
K-nearest neighbors (K-NN)/Local Outlier Factor:
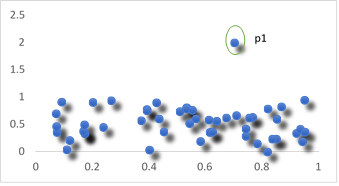
This is the most commonly used algorithm for detecting anomalies. The concept behind this algorithm is very simple and easy to relate with. Suppose, we have a distribution of data as depicted in the picture. It is evident that the point p1 is an outlier.
As a human, we intuitively saw that the nearest neighbor is very far away from the point p1(the local density was low), making it an anomaly. This same intuition powers this algorithm. We calculate the average distance (the local density) of each point with its ‘k’ nearest neighbors. A point will be an outlier if this average distance is significantly higher than the average distances of it’s ‘K’ nearest neighbors.
Although extremely simple logic behind the algorithm, it has performed more robustly and accurately in spotting anomalous data when compared against complex algorithm. Since the model is overly simplified, it cannot handle categorical variable well, as it becomes incredibly difficult to calculate distances for a categorical variable.
Business Example:
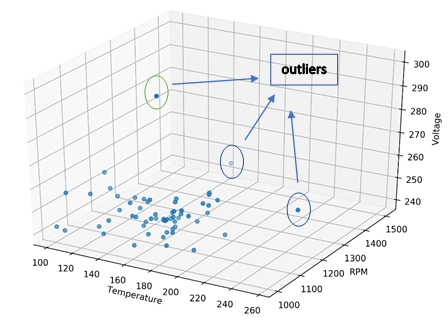
A business has recently upgraded their machineries by incorporating and want to find out reasons for regular machine breakdown. Since there’s a scarcity of good, labeled dataset, unsupervised learning can be leveraged here. Since my dataset consists only of continuous, numerical variables (as depicted in the image above) captured by the sensor, K-NN can be applied to isolate the anomalous observations.
Further inspection by the engineers can narrow down the root cause search. Additionally, it’ll save business millions of dollars if business builds a pipeline that’ll start flagging anomalous observations and hence pro-actively putting machine under maintenance before failure.
Isolation Forest:
“When nothing works, grow decision trees.” Has been a mantra that data scientists have adhered to. K-nearest neighbors although extremely simple in nature is plagued by lot of problems, like the categorical variable handling, runtime, space constraints, all these makes K-NN almost redundant when it comes to real world business use cases. In businesses, we almost always have many categorical variables and millions of data points. To tackle this, researchers developed an algorithm that could—in an unsupervised way—handle these complex problems.
The idea was simple grow a decision tree for all the variables. Once all the data points have passed through the decision tree, and occupies its own node, the anomaly detection becomes easy. The points which lie very close to the root in a terminal node are anomalous since it takes fewer decisions to isolate the point from the rest. To improve the model robustness and efficacy, multiple decision trees (isolation Forest) are grown.
The advantage of this method is like decision tree, isolation forest is nonparametric and makes no assumptions about the data and hence can detect outliers from a mix of categorical and numerical variables. Another advantage is the runtime of the algorithm. It is exponentially faster than iterative K-NN algorithm and hence handle larger datasets.
Business Example:
In the age of e-commerce, we have a trove of structured click stream data, such data is almost always having many categorical variables. If a business wants to analyze why their performance has dipped, anomaly detection finds application. Since the reason for performance can be something that business hadn’t expected or is a new event that has occurred.
Isolation forest finds perfect use here, where my data has a mix of categorical and numerical variables. Implementation of K-NN (distance based) algorithm would, require careful preparation of data, selecting hyperparameters to extract meaningful information out of it. This is tedious and time consuming. On the other hand, Isolation forest has been specifically designed to perform robustly and accurately.
To summarize, depending on the quality and availability of data, a business can either use supervised or unsupervised machine learning model to detect outliers and save millions of dollars if these went unnoticed.
Original Post can be found here